Have you ever wondered where all that electricity that makes everything run like clockwork comes from when we’re leisurely catching up on a show, listening to a song, or burying our heads in work on an airplane?
Is it coming from the sky?
Is it provided by the power company?
Today, let’s go on a “power exploration”, together to open the mystery of the aircraft power supply system.

Aircraft entertainment systems, galley ovens, rudder drive motors, anti-ice systems …… are all large users of electricity on the aircraft, plus a variety of instruments, a variety of lights, seat power supply and other electrical equipment, they all rely on the aircraft’s strong, stable power supply system, so where does the electricity on the aircraft actually come from?
The aircraft power system generally consists of a main power supply, an auxiliary power supply, an emergency power supply and a ground power supply.
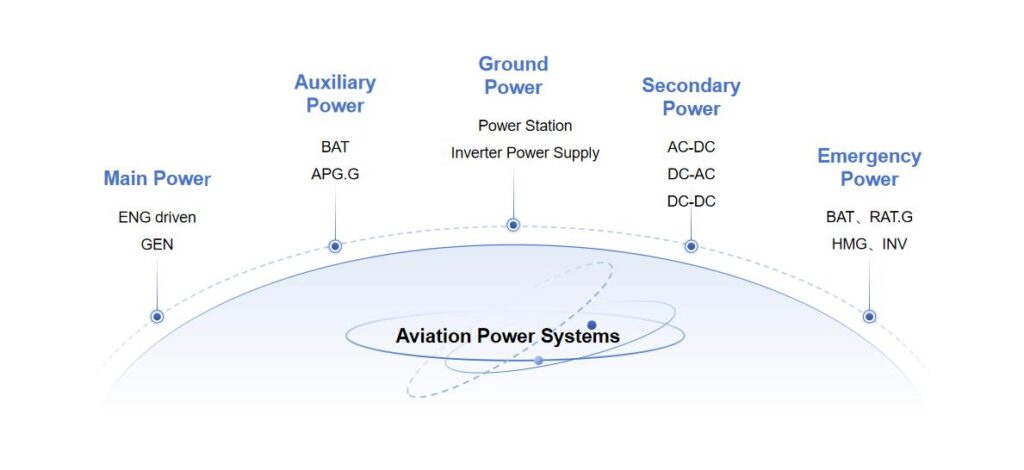
The main power supply – the “power heart” of the airplane
The engine of an airplane is like a Hercules.
It is not only to push the airplane to fly into the sky, through the clouds, but also to take up the responsibility of “power generation”. Whenever this Hercules by burning kerosene rumbling rotation, will drive the generator next to the “little brother”, the mechanical energy into electrical energy.
This is like putting a “power heart” into the airplane. The power distribution system on the airplane is like the “blood vessels” of the human body, responsible for transmitting electrical energy to the electrical equipment, and at the same time managing the electrical load and protecting the electrical equipment.
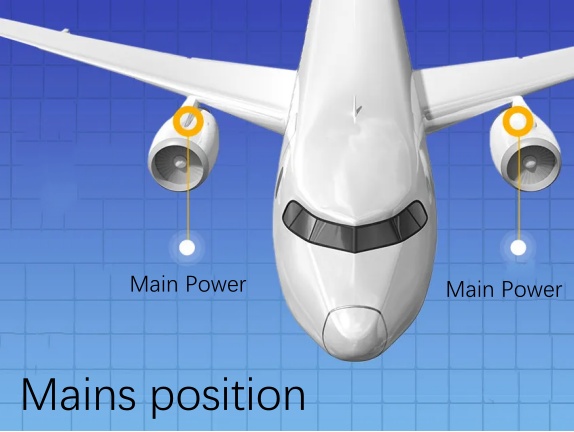

Typically, airplanes are equipped with more than two sets of main power supplies. When any one set of main power fails, the faulty power supply will be with drawn from operation, and the rest of the normal power supply to ensure the normal power supply of all electrical equipment.
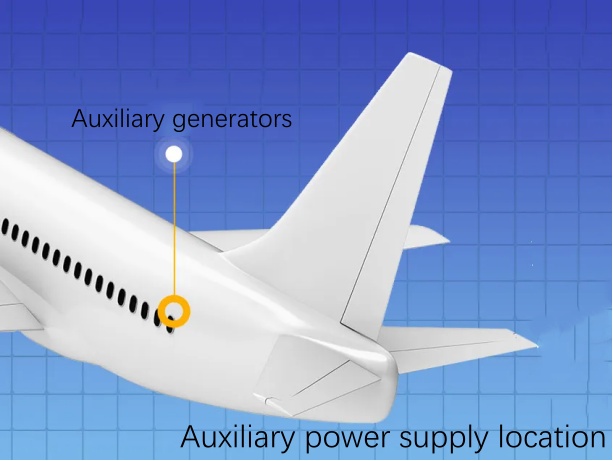
Auxiliary power – “rechargeable” on the ground and in emergencies
The auxiliary power supply comes into play during the ground preparation phase, such as before starting the engines after the aircraft leaves the bridge, or if the main power supply fails!
It may be a small generator or an Auxiliary Power Unit (APU), which is like a “rechargeable battery” that the airplane carries with it. When needed, they can be quickly activated to provide temporary power to the aircraft.
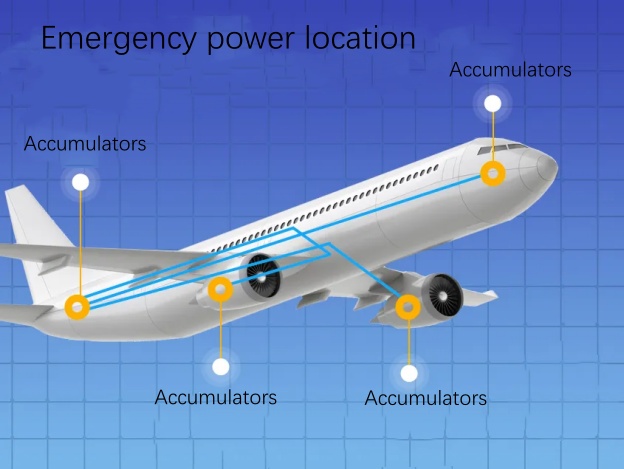
Emergency power supply – the “secret weapon” for a safe return to the air
You may be wondering what happens if the auxiliary power supply goes on strike?
Don’t worry, the emergency power supply will come forward and take over the power supply task to ensure that key equipment such as communication, navigation and emergency lighting can still work normally.
It’s like a “secret weapon” that comes into play at critical moments to ensure our safe return.
So is the electricity on an airplane the same as the electricity you use at home?
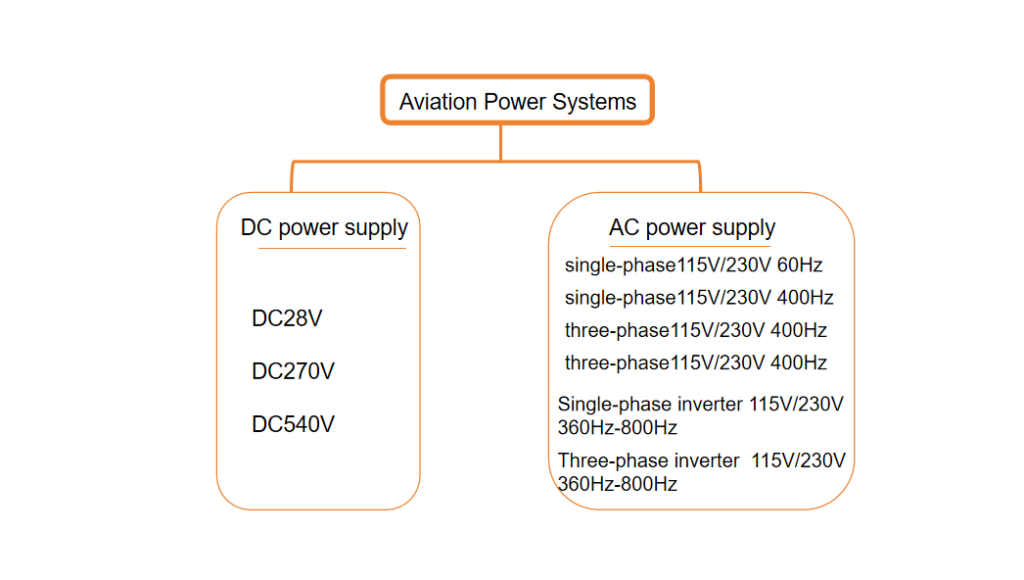
First of all, the voltage and frequency of the power supply on an airplane is very different from the utility power.
Unlike the utility’s 220-volt voltage and 50-hertz frequency, the airplane power supply uses 115-volt voltage and 400-hertz frequency. This kind of electricity is more suitable with the airplane.
Secondly, because the airplane can not be blacked out during the flight, and the quality of electricity is very high, so the power supply system on the aircraft must have a high degree of safety and reliability.
This includes the use of high-quality electrical equipment and wiring, the installation of multiple protection measures and strict maintenance and inspection.


