Variable Frequency Drive: (VFD or VVVF) is an electrical device that uses an inverter circuit to change an industrial-frequency power supply into a variable frequency power supply with variable frequency and voltage, which in turn regulates the speed of a motor.
Types of frequency converter characteristics of many types of frequency converter, categorized in a variety of ways, according to the needs of the use, conversion mode, the nature of the power supply, voltage regulation methods, frequency control and other ways of classification.
I.Classification by use
Frequency inverters can be divided into two categories according to the use of general-purpose frequency inverters and special-purpose frequency inverters.

1.General-purpose frequency converter is in many ways a strong generality of the frequency converter of this type of frequency converter to simplify the system function, mainly for the main purpose of energy saving, mostly small and medium-capacity frequency converter, generally used in pumps, fans, fans, blowers and other occasions that do not have high requirements on the system’s speed regulation performance.

2.Dedicated inverter is designed specifically for a particular aspect or a field of inverter, targeted, with unique features and advantages to better play the role of frequency conversion speed control, generality is poor.
At present, the more common special inverter mainly fan class special inverter, constant pressure water supply (pump) special inverter, machine tool special inverter, heavy-duty special inverter, injection molding machine special inverter, textile special inverter, elevator special inverter and so on.
II.Classification by transformation mode
Frequency converter according to the conversion mode is mainly divided into cross – direct – cross frequency converter and cross – cross frequency converter.

1.AC-DC-AC inverter, also known as indirect frequency converter, in operation, the first frequency AC power through the rectifier circuit is converted into pulsating DC power, and then through the intermediate circuit capacitor smoothing filtering, the inverter circuit copy DC power into frequency and power bank adjustable alternating current to provide draw the load (motor) for variable speed control.
2.AC-AC inverters, also known as direct inverters, directly convert AC power from industrial frequency to AC power with adjustable frequency and voltage and provide it to the load (motor) for variable speed control.
III.According to the nature of the power supply classification inverter according to the nature of the power supply can be divided into voltage-type inverter and current-type inverter
| Typology | Voltage Inverter | Current Inverter |
| Energy storage element | Capacitor | Inductor |
| Circuit configuration | ① Feedback diode: ② DC power supply in parallel with large-capacity capacitors (low-impedance voltage source) ③Four-quadrant operation of the motor requires the use of converter | ①No feedback diode ② DC power supply in series with a large inductance inductance (high impedance current source) ③ Motor four-quadrant operation easily |
| Characterization | ① Overcurrent when the load is short-circuited ② Slower torque response of the inverter ③ High input power factor | ①Overcurrent can be suppressed when the load is short-circuited ② Inverter torque response is fast ③ Input power factor is low |
1.Voltage type inverter is characterized by the intermediate circuit using capacitors as energy storage elements to buffer the reactive power of the load, the DC voltage is relatively smooth, commonly used in the occasion of large changes in load.
2.Current-type inverter is characterized by the intermediate circuit using inductors as energy storage elements to buffer the reactive power of the load, that is, choke current changes, commonly used in load current changes in the occasion, suitable for the need to feed back braking and often forward/reverse rotation of the production machinery.
Voltage inverter and current inverter are not only different in circuit structure, but also different in performance and scope of use.
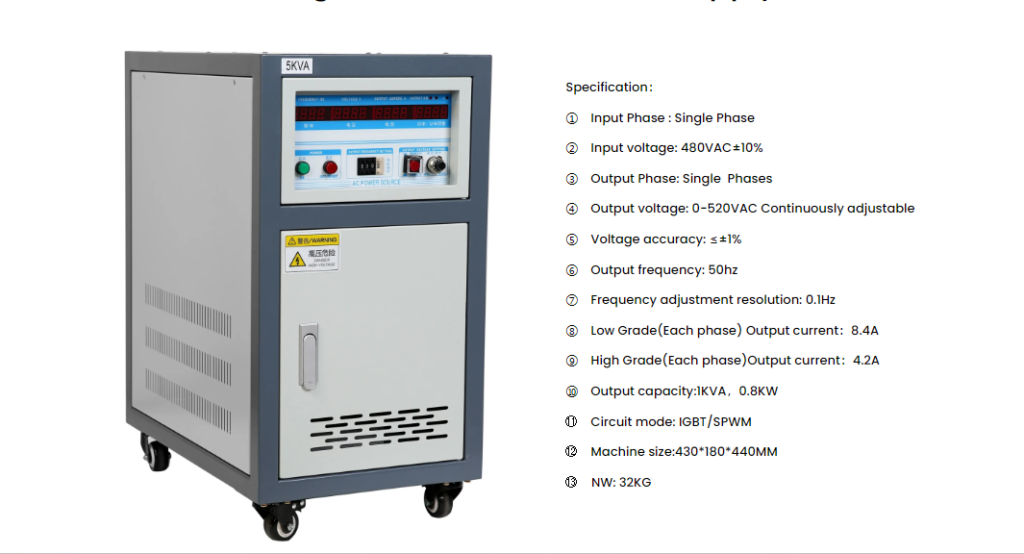
In addition to the above classification, frequency converter can be divided into pressure/frequency (U/f) control frequency converter, frequency control frequency converter, vector control frequency converter, direct torque control frequency converter, etc.
According to the frequency control method, PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation) frequency converter can be divided into PAM frequency converter and PWM frequency converter according to a certain law.
Frequency converter can be divided into PAM frequency converter and PWM frequency converter according to the method of regulating voltage.
PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation, Pulse Amplitude Modulation) frequency converter can be modulated according to a certain law of pulse amplitude of the pulse train.
PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation) inverters modulate the pulse amplitude of a pulse train according to a certain pattern, and the pulse amplitude is controlled by a microprocessor.
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) inverters modulate the pulse width of a pulse train according to a certain pattern. The pulse width is controlled by the microprocessor.
Inverter according to the number of phases of the input current is divided into three into three out, single into three out inverter.
The input and output sides of a three-in, three-out inverter are powered by three-phase alternating current. The input side of a single-input/three-output inverter is powered by single-phase alternating current, and the output side is powered by three-phase alternating current.